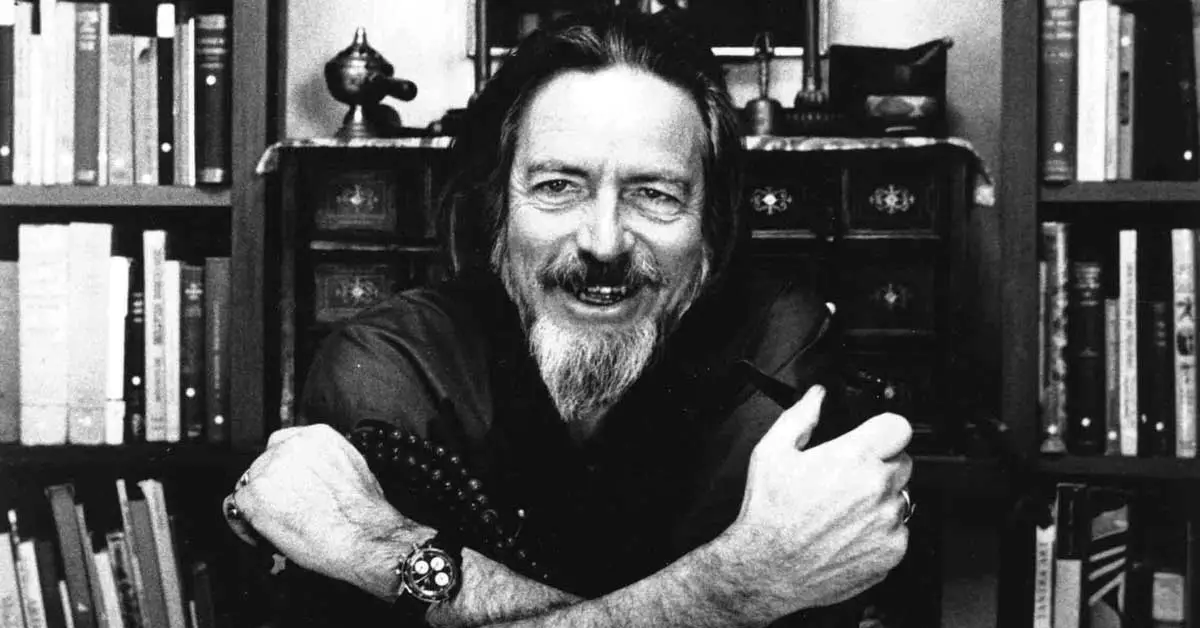
Who is Alan Watts?
Alan Watts (1915-1973) was a prominent figure known for his insights into Eastern philosophy and spirituality. He helped introduce these ideas to Western audiences during the mid-20th century. His work centred on merging Eastern and Western philosophical and spiritual perspectives, often delving into topics like consciousness, the self, and the interconnectedness of existence.
Watts maintained an extraordinary talent for facilitating complex ideas, making them understandable and engaging for a broad audience. His books, such as “The Way of Zen” and “The Wisdom of Insecurity,” continue to impact many readers. He encouraged people to live in the moment, discover their true selves, and show authentic lives. His teachings have had a lasting impact on Western spirituality, mindfulness practices, and the New Age movement.
Watts was a charismatic speaker and an influential writer. His ability to convey profound wisdom in accessible language has made him a revered figure in philosophy and spirituality. He remains celebrated for his role in introducing Eastern philosophies to the West and for his ongoing influence on how individuals explore and understand their existence.
Early Life of Alan Watts
Alan Watts was born on January 6, 1915, in Chislehurst, Kent, England. His early years were marked by an innate curiosity and a profound interest in Eastern cultures and philosophies. As a young boy, he began to explore Buddhism and voraciously read Eastern texts, showing a budding passion for these ideas.
Watts received his education at the King’s School in Canterbury, where he excelled academically. In 1930, at the remarkably young age of 15, he published his first essay on Zen Buddhism, foreshadowing his future intellectual pursuits.

At the age of 20, Watts scratched the Atlantic to study at the Seabury-Western Theological Seminary in Illinois, originally with the purpose of becoming an Episcopal priest. However, he soon realised that the traditional teachings of Western Christianity did not resonate with his burgeoning attraction to Eastern spirituality. Consequently, he left the seminary but remained in the United States, where he continued to delve into and study Eastern philosophies.
The Career of Alan Watts
Alan Watts had a diverse career that contained philosophy, writing, and public speaking, significantly affecting Western comprehension of Eastern philosophies.
After leaving theological studies in the United States, Watts became a prolific writer and speaker. He gained recognition as a philosopher bridging Eastern and Western thought in the 1930s and 1940s. He started sharing his insights on the radio and in essays, primarily centred on Eastern philosophy.
In the 1950s, Watts gained widespread acclaim with his radio show, “Way Beyond the West,” which allowed him to delve deeply into Eastern philosophies and spirituality. His unique talent for conveying intricate concepts in an understandable manner made him a highly sought-after speaker. During this period, he authored influential books like “The Way of Zen” (1957) and “Nature, Man and Woman” (1958), cementing his status as a preeminent interpreter of Eastern thought for Western audiences.

Watts relocated to California in the early 1960s, where he became associated with the counterculture movement of the era. He continued to deliver lectures and prolifically wrote on subjects ranging from meditation to the essence of consciousness. His lectures attracted large audiences, and he frequently spoke at universities and cultural institutions.
Throughout his career, Watts emphasized the importance of living in the present moment and discovering one’s genuine self. He encouraged individuals to break free from societal conventions and live authentically. His work deeply influenced the emerging mindfulness movement and the New Age spirituality movement of the 1960s and 1970s.
Personal Life of Alan Watts
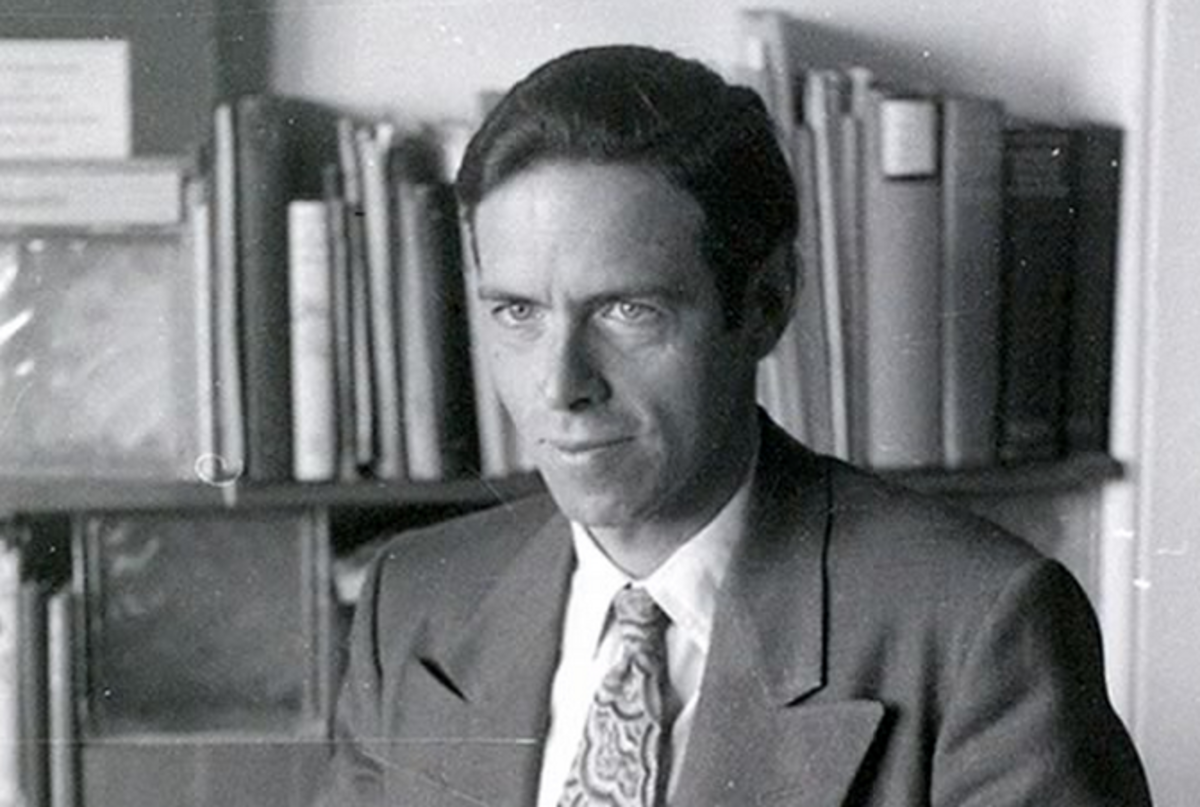
Alan Watts led a rich personal life, characterized by multiple marriages and a connection to the counterculture of the 1960s. He married Eleanor Everett and had two daughters before divorcing her. His second marriage was to Dorothy DeWitt, with whom he had a collaborative partnership in various projects, but this marriage also ended in divorce.
His third and final marriage was to Mary Jane Yates King in 1964, which endured until his death in 1973. Mary Jane played an essential role in supporting Watts’s work, helping organize his lectures and writings.

Watts spent a significant part of his life in California, where he became associated with the counterculture movement. He was known for his exploration of Eastern spirituality and an interest in psychedelic substances, both of which were popular among counterculture figures of that era.
Watts was also a dedicated practitioner of meditation, advocating for mindfulness practices. His personal life reflected his commitment to living authentically and aligning with his philosophical beliefs, which emphasized the importance of the present moment and the interconnectedness of all life.
Physical Statistics of Alan Watts
| Height | 5’10” (178 cm) |
| Weight | 160 lbs (73 kg) |
| Eye Color | Blue |
| Hair Color | Brown |
| Build | Average |
Net Worth of Alan Watts
Alan Watts’ exact net worth at the time of his death in 1973 remains undisclosed, as he wasn’t particularly renowned for accumulating substantial wealth. His prominence was primarily rooted in his contributions to philosophy and spirituality, especially in introducing Eastern philosophies to the Western world.
Watts supported himself through various means, such as writing, public speaking engagements, and workshops. He authored several books and delivered lectures, activities that generated income and helped sustain his livelihood. Notably, his books like “The Way of Zen” and “The Wisdom of Insecurity” continue to be published and contribute to his legacy.
Furthermore, Watts’ association with the counterculture movement of the 1960s and his exploration of subjects like meditation and consciousness expanded his influence and popularity.

While the precise details of his financial worth may remain undisclosed, the enduring impact of Alan Watts on the realms of philosophy and spirituality is undeniable. His legacy persists through his writings, recorded lectures, and the lasting influence of his ideas on topics such as mindfulness, meditation, and the pursuit of a more profound and meaningful existence.
Interesting Facts about Alan Watts
- An early fascination with Buddhism, he wrote his first Zen essay at 15.
- He was ordained as an Episcopal priest but left due to philosophical differences.
- Authored over 25 books on Eastern philosophy, psychology, and consciousness.
- Gained popularity through his radio show “Way Beyond the West.”
- Influenced the counterculture movement of the 1960s.
- Studied and practised Zen Buddhism in the United States.
- British by birth, retained a British accent.
- Skilled in playing musical instruments like piano and violin.
- Emphasized the limitations of the ego and living in the present moment.
- His work continues to popularize Eastern philosophies in the West, remaining influential today.
FAQs about Alan Watts
Who was Alan Watts?
Alan Watts was a renowned philosopher, writer, and speaker known for his exploration of Eastern philosophy.
When and where was Alan Watts born?
Alan Watts was born on January 6, 1915, in Chislehurst, Kent, England.
What is Alan Watts known for?
He is celebrated for popularizing Eastern philosophies, particularly Zen Buddhism and Taoism, in Western cultures.
How did Alan Watts become popular?
Alan Watts gained fame through his engaging radio broadcasts, numerous books, and captivating lectures, making complex philosophical ideas accessible to the public.
Did Alan Watts practice Zen Buddhism?
Yes, he practised Zen Buddhism and studied under various Zen masters, including D.T. Suzuki.
What are some famous books by Alan Watts?
Notable works by Alan Watts include “The Way of Zen,” “The Wisdom of Insecurity,” and “The Book on the Taboo Against Knowing Who You Are.”
How did Alan Watts contribute to the counterculture movement?
Alan Watts became associated with the counterculture movement in the 1960s, as his teachings on mindfulness, consciousness, and societal nonconformity resonated with the era.
What was Alan Watts’ perspective on the ego?
Watts emphasized the limitations of the ego and encouraged living in the present moment, ideas that continue to shape mindfulness practices.
How many times was Alan Watts married?
Alan Watts was married three times in his lifetime.
What is Alan Watts’ lasting legacy?
Alan Watts’ legacy endures through his writings, recorded lectures, and profound influence on Western spirituality, mindfulness practices, and the widespread acceptance of Eastern philosophies.
Conclusion
Alan Watts is an iconic figure in the realm of philosophy and spirituality. His life and work are characterized by an insatiable curiosity for profound philosophical inquiries and a relentless commitment to bridging the gap between Eastern and Western philosophies.
Watts possessed a unique talent for articulating intricate concepts in a manner that resonated with a wide audience, rendering him an engaging orator and prolific writer. He emphasized the significance of living in the present, transcending ego-driven constraints, and recognizing the interconnectedness of existence—a message that continues to captivate those on a quest for authenticity and purpose.
His influence stretched far beyond academic circles, permeating the counterculture movement of the 1960s. Watts’ ideas struck a chord with individuals challenging societal norms during this era of cultural transformation.